1. Basic definition and origin
(1) Yoga
Yoga originated in ancient India and is a comprehensive system that combines philosophy, religion and movement, aiming to achieve a balance between body, mind and soul through asana, breathing (Pranayama) and meditation (Dhyana). Its core goal is to improve flexibility, strength and inner peace, and focus on the philosophical concept of "unity of body and mind"

(2) Pilates
Pilates was founded by Joseph Pilates in the 1920s. It was originally centered on the "Contrology" and emphasized the strengthening of core muscle groups through precise movements and improving body shape and functionality. Its goal is more towards physical strength, stability and recovery, and it involves less spiritual practice.
2. Core Difference Comparison
| Comparison Dimensions | Yoga | Pilates |
| Training goals | Body and mind balance, flexibility improvement, stress relief, meditation | Core muscle strengthening, posture correction, sports injury rehabilitation |
| Breathing method | Abdominal breathing (inhale through nose and exhale through mouth), deep, long and slow | Transverse chest breathing (inhale through nose and exhale through mouth), activate core muscles |
| Action Features | Static stretches (e.g. Downward Dog) Flow sequences (e.g. Sun Salutations) | Dynamic repetitions (e.g. 100 taps) Small amplitude precision control |
| Calorie consumption | About 200 kcal/hour (normal temperature yoga) | About 400 kcal/hour (machine Pilates) |
| Philosophical Background | The Eightfold Path of India (including moral discipline and spiritual practice) | Six principles of modern sports science (focus/control/core, etc.) |
| Equipment Dependence | Low (mainly bodyweight training) | High (requires professional equipment to provide resistance) |
3. Differences in equipment usage
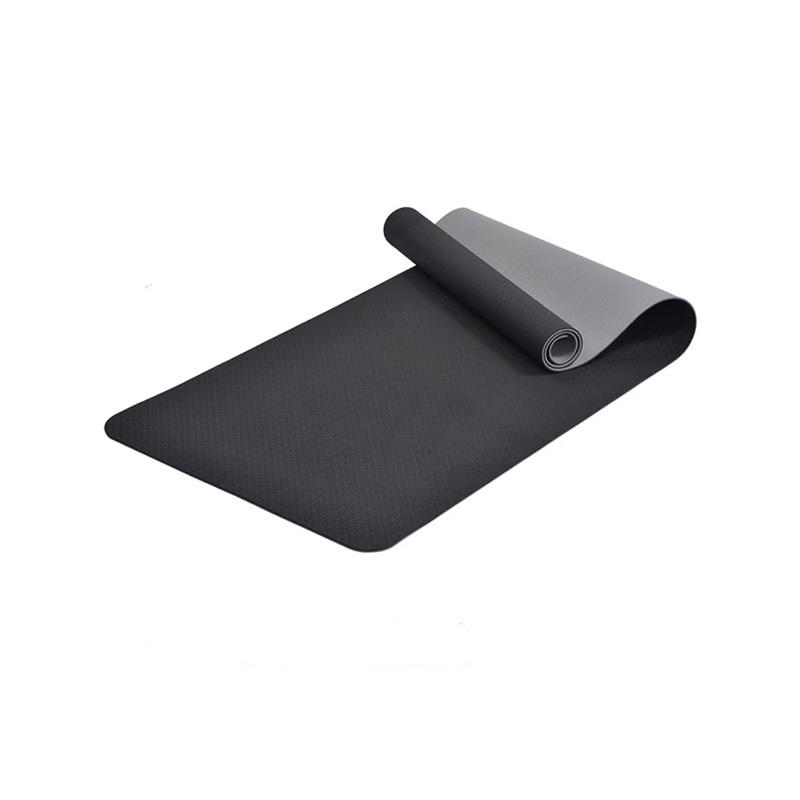
(1)Yoga Equipment
|
The yoga mat is the basis of yoga practice, providing cushioning and support, suitable for a variety of schools.
|
 |
| Function: Used to adjust the height of the pose to help beginners or practitioners who need additional support. Applicable scenarios: Suitable for beginners, pregnant women or poses that require assistance (such as baby pose, triangle pose). |
 |
| Function: Enhance muscle control through elastic stretching, suitable for dynamic stretching and balance training. Applicable scenarios: Suitable for postures that require additional support. |
 |
| Function: used for balance training, improving core stability, and providing spinal relaxation. Applicable scenarios: suitable for home practice, core training and flexibility improvement. Type: including standard yoga balls (28 inches) and thickened explosion-proof yoga balls (suitable for home use). |
 |
Other auxiliary tools
| Yoga Roller is mainly used for self-myofascial relaxation. By rolling the body on the foam roller, you can deeply press and relax tense muscles and fascia, effectively relieve muscle soreness and knots, and improve flexibility and joint mobility. It is often used for warm-up before exercise and recovery after exercise. It is an ideal auxiliary tool for relieving muscle fatigue and accelerating body repair. |  |
| Yoga Wheel is mainly used to assist yoga practice, especially deep backbends. It can provide stable support to help practitioners safely open the chest, stretch the spine, and deepen the range of backbends. In addition, yoga wheels can also be used for balance training, core strength challenges, and provide assistance or local massage in certain asanas to help practitioners explore a wider range of asana possibilities. |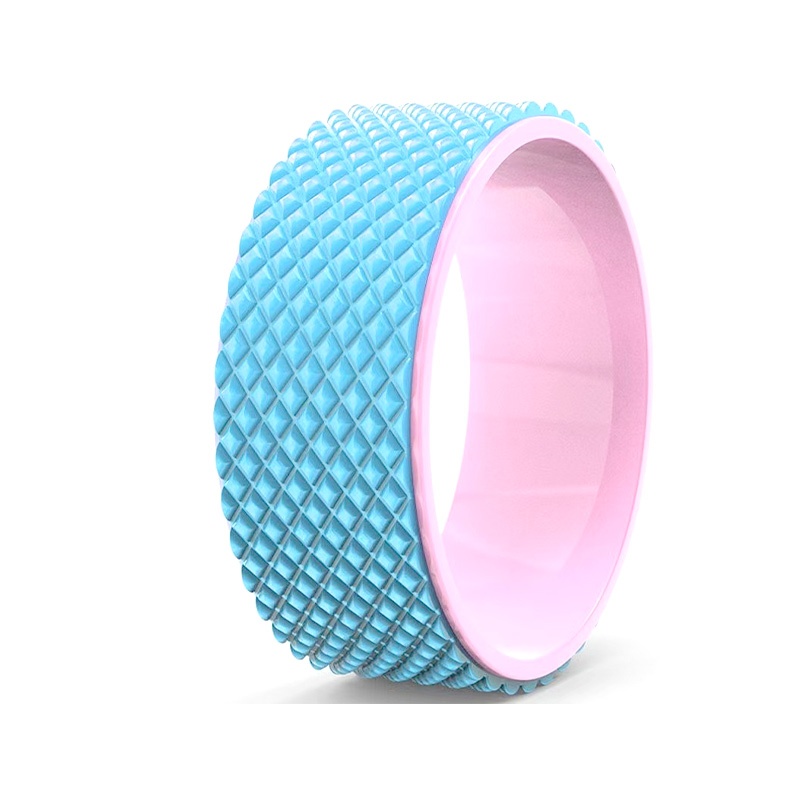  |
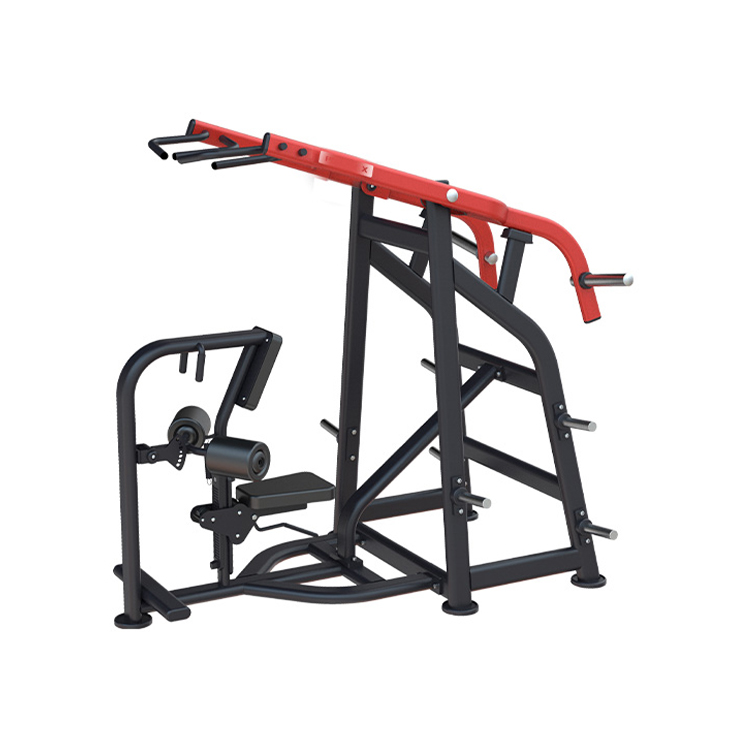
(2)Pilates Equipment
| The Pilates Reformer is one of the most representative equipment in Pilates exercise. It can effectively enhance core strength, improve flexibility, coordination and body control, while helping to correct poor posture. It is suitable for a wide range of people from rehabilitation to high-performance training. |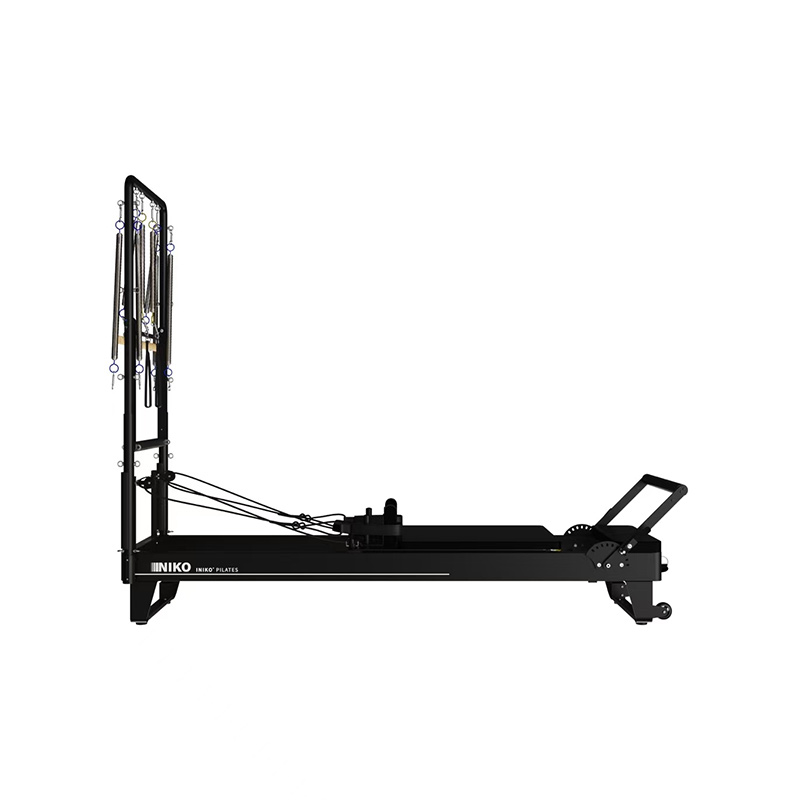  |
| The Pilates Circle, also often called the Magic Circle, is used to increase muscle activation and strengthening. During practice, whether you hold it between your legs, press it with your hands, or place it on other parts of your body, the circle will provide inward or outward resistance. This resistance can help practitioners recruit deeper muscles in the core, inner thighs, buttocks, arms, and chest, improving strength, endurance, and control. |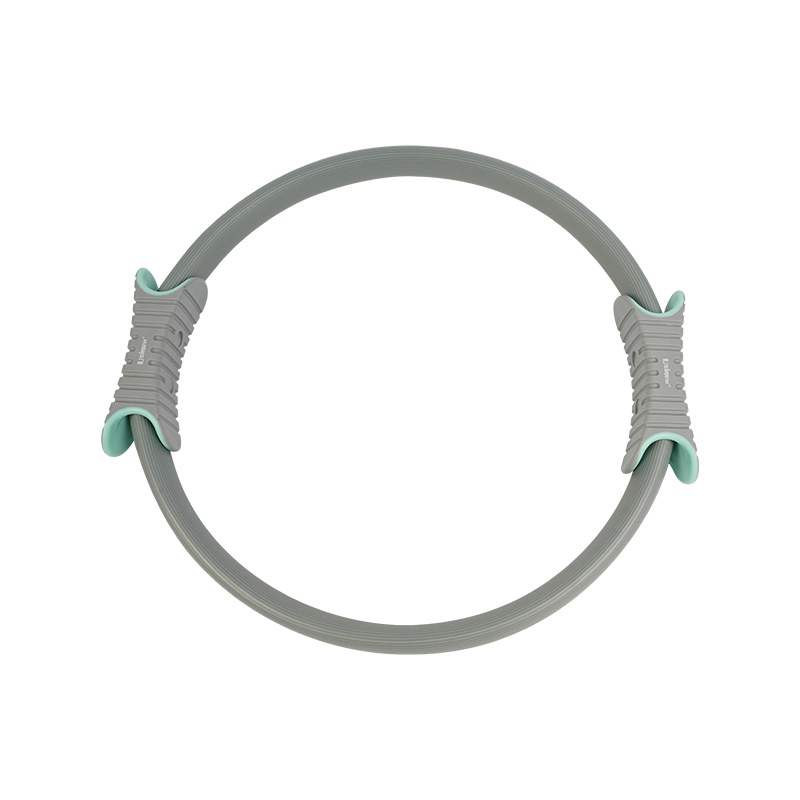  |
Other auxiliary tools
| Trapeze Table | Wunda Chair | Ladder Barrel |
| Function: Upper limb and back training through hanging device, strengthening arm and core strength. Applicable scene: Suitable for upper limb training and core stability exercises. |
Function: Training body control, balance and strength through low-impact method, suitable for precision training of various parts. Applicable scene: Suitable for core training, balance exercises and flexibility improvement. |
Function: Strengthen leg and back strength through the combination of ladder and roller. Applicable scene: Suitable for leg training and core stability exercises. |
4. Equipment selection suggestions
| Equipment Type | Target Group | Core Features | Applicable scenarios |
| Yoga mat | Beginners, home exercisers | Provides cushioning and support | Home, gym, outdoor practice |
| Yoga Blocks | Beginners, pregnant women | Adjusts posture height | Posture assistance |
| Yoga straps | Advanced users, users who need to stretch | Strengthens muscle control | Dynamic stretching, balance training |
| Yoga balls | Home users, core trainers | Improves balance and core stability | Home practice, core training |
| Core mat | Professional trainers, rehabilitators | High-intensity core training and precise control | Professional gym, Pilates studio |
| Pilates ring | Postpartum mothers, home users | Core, hip and pelvic floor muscle training | Home practice, upper limb training |
5. Training goals and effects
(1) Yoga
Goal: Improve flexibility, balance and psychological quality, and achieve physical and mental balance through meditation and breathing regulation.
Effect: Improve posture, relieve stress, enhance visceral function, suitable for long-term practice to achieve physical and mental harmony.
(2) Pilates
Goal: Strengthen core muscles, improve posture, enhance functional strength, especially for the protection of the spine and joints.
Effect: Quickly shape and correct posture problems, suitable for users who are recovering from sports injuries or seeking efficient training
6. Breathing method and movement design
(1) Breathing differences
Yoga: Adopts a breathing pattern of inhaling through the nose and exhaling through the nose, emphasizing the synchronization of breathing and movement to promote energy flow and meditation
Pilates: Adopts a breathing pattern of inhaling through the nose and exhaling through the mouth, focusing on the coordination of breathing rhythm and movement to enhance core control
(2) Action Differences
Yoga: Movements are mostly static or slow-flowing, imitating natural postures (such as cat-cow pose and downward dog pose), emphasizing stretching and balance.
Pilates: Movements are dynamic and coherent, combined with machine resistance, emphasizing the accuracy and control of movements
7. Course types and diversity of schools
(1) Yoga:
There are many schools: including Hatha Yoga (basic flexibility), Ashtanga (strict sequence), Flow Yoga (smooth movements), Yin Yoga (deep stretching), etc., suitable for different needs.
Course format: can be combined with meditation, chanting (such as "Om") and philosophical discussion to enhance the sense of ritual.
(2) Pilates:
School concentration: mainly focusing on core training, common schools such as "Classic Pilates" (Reformer), "Functional Pilates" (Functional Pilates), etc., emphasize the precision of movements.
Course format: mostly equipment-assisted training, suitable for advanced people, some courses combine yoga elements (such as "Yoga Pilates Hybrid Class")
8. Conclusion
The core difference between yoga and Pilates is that yoga focuses on physical and mental balance, flexibility improvement and meditation, and emphasizes the unity of body and mind through freehand exercises (such as yoga mats, yoga bricks) and slow-flowing postures. It is suitable for users who pursue spiritual core and daily relaxation; while Pilates aims at scientific training and functional strength, relies on equipment (such as Pilates beds, elastic bands) for resistance training, and focuses on the precise control of core muscles and posture correction. It is more suitable for groups that need to shape, rehabilitate or improve sports performance.
There are also significant differences between the two in breathing methods, movement design and applicable scenarios. Yoga pays more attention to breathing rhythm and meditation, while Pilates strengthens core stability through dynamic resistance. When choosing, you need to combine your personal goals: if you pursue physical and mental balance, yoga is more suitable; if you need functional training or posture correction, Pilates has more advantages.

 ENG
ENG
 English
English Français
Français Español
Español عربى
عربى